Phase Change Energy Storage Technology
Heat and Cold storage with Phase Change Material (PCM) – An Innovation for Storing Thermal Energy and Temperature Control
- What is phase change energy storage technology?
- Sensible Heat vs Latent Heat
- Phase Change Materials (PCM)
- Advantage of phase change energy storage
- Economical and Environmental Benefits
WHAT IS PHASE CHANGE ENERGY STORAGE?
Thermal energy storage (TES), also called heat and cold storage, allows the storage of heat or cold to be used later. To retrieve the heat or cold after some time, the method of storage needs to be reversible. Sensible Heat and Latent Heat are common methods of storing thermal energy.
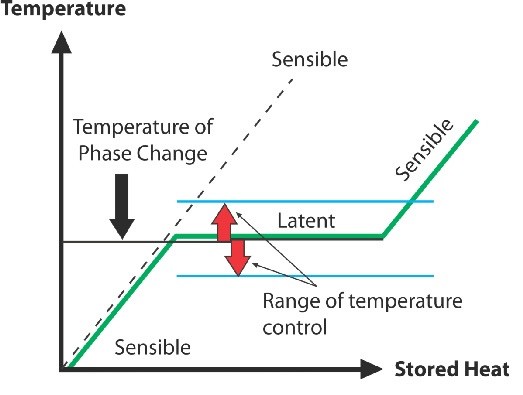
WHAT IS SENSIBLE HEAT STORAGE? AND WHAT IS LATENT HEAT STORAGE?
The most common way to store thermal energy is as sensible heat. As shown in the figure below, heat transferred to the storage medium leads to a temperature increase of the storage medium. A common example is hot water storage for domestic heating and hot water.
The phase change of solids and liquids by melting and solidification can store large amounts of heat or cold. Melting results in a small volume change, usually less than 10%. If a container can fit the material in its liquid state, the pressure does not change significantly. Consequently, the melting and solidifying of the storage material proceed at a constant temperature. Upon melting, the heat transfers to the storage material and remains at a constant temperature. This is the phase change temperature. Further transfer of heat after melting results in sensible heat storage. The heat supplied upon melting is latent heat, and the process is latent heat storage.
Sensible Heat vs. Latent Heat

Temperature Control During Phase Change Energy Storage
PHASE CHANGE MATERIAL (PCM)
Inorganic PCM are engineered hydrated salt solutions made from natural salts and water. The chemical composition of the salts is varied in the mixture to achieve the required phase change temperature. Special nucleating agents added to the mixture minimize salt separation and supercooling, which are characteristics of hydrated salt PCM. Salt Hydrates are non-toxic, non-flammable, and economical.
Bio-based PCM are organic materials that are naturally existing fatty acids such as vegetable oil. Based on their chemical composition, their phase change temperature can vary. These products are non-toxic, non-corrosive, and have infinite life cycles. They can be expensive as well as flammable at high temperatures.
Organic PCM are naturally existing petroleum bi-products that have a unique phase change temperature. Since major petrochemical companies manufacture these products, their availability can be limited. They can be toxic, flammable, and expensive. They have infinite life cycles and the price varies with changes in global petroleum prices.
ADVANTAGES OF PHASE CHANGE ENERGY STORAGE
- Thermal energy stored at the temperature of process application.
- Store thermal energy as latent heat which allows higher thermal energy storage capacity per unit weight or material without any change in temperature.
- Store thermal energy from a thermal or electrical energy source and use when needed.
- Stored thermal energy is portable and rechargeable.
ECONOMICAL & ENVIRONMENTAL BENEFITS
- Store natural thermal energy for facility heating and cooling needs. Reduced energy demand reduces carbon footprint.
- Save on energy cost and help stabilize grid load by storing thermal energy during off demand hours and using it during peak demand hours.
- Shifting heating and cooling loads reduces peak time stress on the equipment, resulting in reduced operating and maintenance costs.
- This technology leads to HVAC equipment sized for the average load instead of the peak load.
